Selenium is the pre-eminent open source software test automation system in the world of testing. Part of the rise in popularity of selenium was the addition of Selenium grid which allows for parallel test case execution, thus significantly reducing time for regression. In addition, selenium grid enables multiple parallel environments to be simultaneously tested. This article starts with a short overview of selenium and then dives into depths of Selenium Grid.
The first automation tool that comes into our mind when we listen to the word “Automation” is “Selenium”. It is the most widely used automation testing tool for testing web-based applications. The organizations want to shorten the test suite automation cycle duration, and Selenium GRID is architectured to address this core problem. Webomates CQ framework supports distributed execution while using advanced elastic features in AWS and exhibits AI-based reporting. Webomates has a patented technology for multi channel testing, which reduces the test suite execution time immensely while getting maximum code coverage.
Selenium is a free/open Source Automation testing suite for testing web applications. It was developed by ‘Jason Huggins’ in 2004.
Selenium is a software suite with following components:
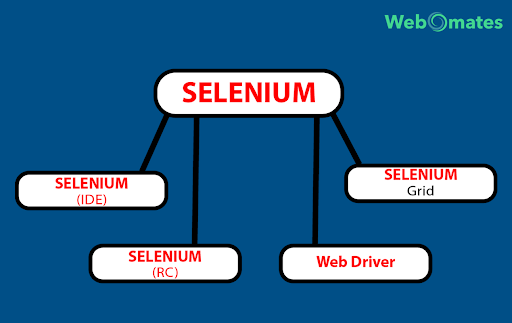
Selenium IDE: Selenium IDE enables the browser for record and playback. It is supported only on the Firefox browser.
Selenium RC (Remote Control): It resolves JavaScript’s ‘Same Origin Policy Issue’ and is a server that acts as an HTTP proxy and enables the browser to believe that Selenium Core and the web application come from the same domain.
WebDriver: it is a cross-Platform testing framework that can control the browser from OS Level. It is supported by multiple browsers, Chrome, Internet Explorer, Firefox, etc.
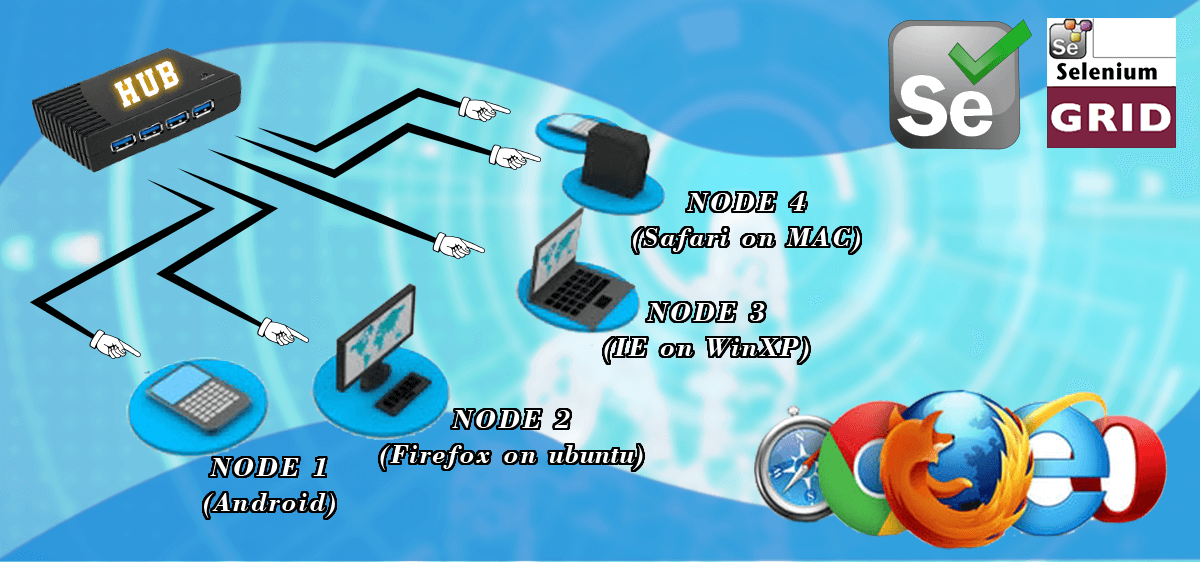
Selenium GRID: Selenium GRID was developed by Patrick Lightbody. Initially, he named it “Hosted QA”. It was primarily developed for minimizing the test execution time. Its architecture (hub-node model) enables the user to run multiple test cases simultaneously in a distributed environment (on nodes). This is mainly used by organizations having needs to execute large regression suites on the cross-platform environment on a recurring basis.
Now that we have seen a quick overview of Selenium, let’s explore more about Selenium GRID.
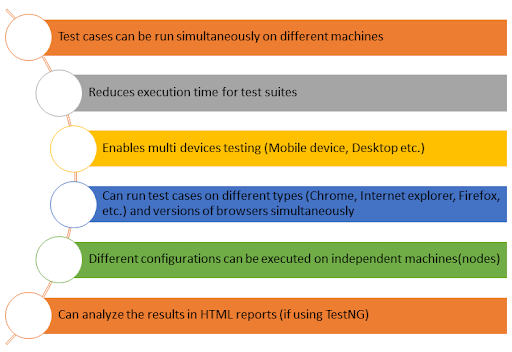
Selenium GRID is a feature of Selenium, that allows running test cases in parallel. It is a network of connected test case execution machines. Further, it enables running test cases on different Operating systems, browsers, configurations, etc. based on the application and requirement. Selenium GRID reduces the time of test execution multi-fold. It is based on a distributed (Hub-Node) model.
Following diagram represents Selenium GRID architecture.
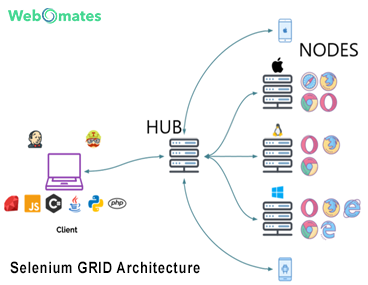

Hub: Orchestrator/Master/Central Point of test cases. There is only one Hub in a GRID. It communicates and orchestrates test execution on all nodes simultaneously.
Node: Any test machine that is added to the hub, that performs test executed based on a command from Hub. Nodes run their Selenium Browser Drivers. Nodes are Independent of each other.
Execution: To run test scripts on the Grid, one should use the DesiredCapabilities and the RemoteWebDriver objects.
While executing test cases locally, the WebDriver client libraries talk to theWeb Browser Driver directly. Now, when you try to execute your tests remotely, the WebDriver client libraries talk to the RemoteWebDriverserver and the server talks to either the Firefox Driver, IE Driver, or Chrome Driver, whichever the WebDriver client asks for.

Reporting goes hand in hand with Selenium Grid. All the test results and test evidence are collated into a comprehensive report for user view. Also, one can use Plugins or custom reporters to view reports in user friendly HTML/Excel formats.
Individual Nodes send their results to Hub, which are then consolidated and reported by Hub. Hub will decide to which node the request is to be sent for execution. This is done based on the Desired Capabilities provided to Hub. We need to mention “Desired Capabilities” in our code. ‘Desired Capabilities’ are mentioned in the class called ‘Remote WebDriver’. Remote WebDriver enables us to execute our code on remote machines. ‘Desired Capabilities’ tells the hub that I want my code to be executed in this particular type of environment.
Desired Capability comprises of the following three components:
Once the hub receives the Desired Capabilities, it selects a suitable node that meets the criteria mentioned in ‘Desired Capabilities’. Hub and node connection is also done on the basis of IP of hub and node. Hub uses JSONWire protocol through HTTP (also referred to as WebDriver protocol) for communication with nodes. This is a REST call we are passing i.e. simple REST API or web service will be called. In case none of the nodes qualify with the requirement, it gives back an error stating unavailability of the desired OS/Browser/Version.
On that node (which already has required browser driver installed), that particular browser will be launched, followed by the execution of browser-specific commands as per the test cases.
The results of the test case execution are returned by nodes to the Hub. Hub will consolidate the results and publish them as required.
Version and Installation of Selenium Grid: To read more about click here

Similar to Selenium, Selenium GRID also does not support the testing of Desktop applications.
However at webomates we have solved this problem by integration with “Visual Image Match” tool that results in our being able to test client desktops too.
Conclusion: Selenium GRID is suitable to shorten the test suite execution times and run test cases on a multi-platform cross-browser environment. Webomates product, ‘Webomates CQ’, follows a Distributed Framework which not only enables the users to execute distributed, multi-platform cross-browser test suite but also enables plug-n-play (/SAAS based) framework with run time, user-friendly reporting. Using the AI-based framework, Webomates CQ creates, maintains, executes test cases. Post regression execution the platform analyzes the execution report and generates defects.The multi-fold reduction in execution time by Webomates CQ enables our global customers to run large regression suites in CI/CD chains, with nightly builds or in 24 hours includes exploratory testing. Click Here to know more about how Webomates CQ can fit seamlessly in your current test execution strategy. After analyzing your ecosystem, we can recommend the most suitable implementation approach. Accordingly, we may enable you to deploy Webomates CQ in your lab/VM based / Cloud-based environment.
Test Smarter, Not Harder: Get Your Free Trial Today!
Start Free Trial
Leave a Reply